
As already mentioned, it supports conceptual, logical, and physical modeling. Navicat Data Modeler supports three standard notations: Crow’s Foot, IDEF1x and UML.Īlthough easy to use, Navicat Data Modeler is a powerful data modeling and database design tool. The tool offers a lot of flexibility, so you can create, modify, and design models in a user-friendly manner and the way you like.
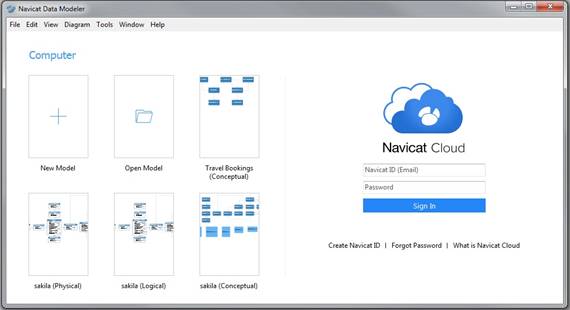
The interface enables the user to clearly see the relationships, entities, and attributes at a high level, as well as the ability to zoom in to see details (see Figure 2).įigure 2. A Logical Data Model in Navicat Data Modeler Figure 1 shows a portion of larger logical data model for a university application.įigure 1. Navicat Data Modeler provides a rich interface for visually designing and building conceptual, logical and physical data models. Navicat Data Modeler is designed to be used by data architects and modelers (but it can, of course, be used by DBAs, too).Ī good data modeling tool provides the user with an easy-to-use palette for creating data models, and Navicat Data Modeler succeeds in this area. We have looked at other Navicat products in this blog before ( 1, 2, 3), but those were performance and DBA tools. Which brings us to the primary focus of today’s blog post: Navicat Data Modeler. The physical data model transforms the logical model into a physical implementation using a specific DBMS product such as Oracle, MySQL or SQL Server. A logical data model provides an in-depth description of the data independent of any physical database manifestations. Furthermore, the domain or data type of each attribute must be defined. The logical data model consists of fully normalized entities with all attributes defined. It depicts a high-level, business-oriented view of information. A conceptual data model is generally more abstract and less detailed than a complete logical data model. The modeling process requires three phases and types of models: conceptual, logical and physical. Even with today’s modern infrastructure that includes databases with flexible schemas that are applied when read (instead of the more traditional method of applying the schema on write), you still need a schema and an understanding of the data in order to do anything useful with it. Data modeling asks the question “What?” instead of the more common data-processing question “How?”Īs data professionals, it is important that we understand what the data is and what it means before we attempt to build databases and applications using the data. The data modeling process results in the discovery and documentation of the data resources of your business. Data modeling is the process of analyzing the things of interest to your organization and how these things are related to each other.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
